Learn to call an API¶
One of the primary use cases for a Pack is to integrate with an external API, allowing users to bring in data or functionality not native to Coda. In this tutorial you'll create a formula that makes a request to an API and uses the response to calculate the result.
Goal
Build a ToUSD formula that uses an external API to convert currency values to US dollars.
Before starting this tutorial, make sure you have completed:
- One of the Get started tutorials, either In your browser or On your local machine.
- The Basic formula tutorial, which covers how to build formulas.
Select the API¶
When building a Pack around data from an external API, it's usually best to first select the API and examine its capabilities and requirements, as those may have a large influence on the design of your formula.
For this Pack we'll be using the API provided by ExchangeRate-API, which has a free plan that doesn't require any keys or credentials. As shown in their documentation, you can get the latest exchange rates using the following URL:
https://open.er-api.com/v6/latest/CAD
The endpoint returns a JSON response, which includes the conversion rate for all of the currencies it supports:
{
"result": "success",
"base_code": "CAD",
"time_last_update_utc": "Wed, 06 Dec 2023 00:02:31 +0000",
// ...
"rates": {
"AED": 2.704071,
"AFN": 52.369208,
// ...
"USD": 0.736528,
}
}
Here we see that one Canadian dollar converts to about 0.74 US dollars (at the time this request was made.) This will provide us the information we need to build our formula.
Design the formula¶
Looking at the inputs and outputs to the API, we could imagine a formula that takes an amount and currency code as input and returns a converted amount as a number.
ToUSD(100, "CAD") ==> $79.65
Write the code¶
Now that we've got our API selected and formula designed we're ready to dive into coding.
Add the standard Pack boilerplate, including the import and Pack declaration. Define a formula called For the result type use Hard-code the ToUSD which takes an amount and from parameter.Number, with the value hint Currency to get it to render with a dollar sign.execute function to return zero for now, which we'll replace later with the real value fetched from the API.import * as coda from "@codahq/packs-sdk";
export const pack = coda.newPack();
pack.addFormula({
name: "ToUSD",
description: "Convert a currency to US dollars.",
parameters: [
coda.makeParameter({
type: coda.ParameterType.Number,
name: "amount",
description: "The amount to convert."
}),
coda.makeParameter({
type: coda.ParameterType.String,
name: "from",
description: "The currency to convert from."
}),
],
resultType: coda.ValueType.Number,
codaType: coda.ValueHintType.Currency,
execute: async function ([amount, from], context) {
// TODO
return 0;
},
});
With the formula scaffold in place, let's focus in on the First we'll need to build the URL to send the request to. We do this by concatenating the base URL with the currency code the user supplied.execute function.execute: async function ([amount, from], context) {
let url =
"https://open.er-api.com/v6/latest/" + from;
},
To make the request to the API you need to use the Set the HTTP method to Fetcher requests are asynchronous, meaning that The response from the API is captured in the fetcher object, which lives within the formula's context. Its fetch method takes a set of key-value pairs that configure the request.GET and the URL to the one we previously constructed.fetch only starts the request, but doesn't wait for it to finish. To do that use the await keyword, which tells our code to pause until the API responds.response variable, which you'll use later.execute: async function ([amount, from], context) {
let url =
"https://open.er-api.com/v6/latest/" + from;
let response = await context.fetcher.fetch({
method: "GET",
url: url
});
},
The fetcher response includes lots of information about what the API sent back, but in this case we're interested in the Referring back to the raw API response we saw earlier, the information you need is in the The API returns the conversion rate for a single unit of currency, so before returning it you'll need to multiply it by the amount the user specified.body only. When Coda detects that the response is JSON it will automatically parse it for you.rates sub-object under the key USD. Since the response is already parsed you can "dot" into that value and use it.execute: async function ([amount, from], context) {
let url =
"https://open.er-api.com/v6/latest/" + from;
let response = await context.fetcher.fetch({
method: "GET",
url: url
});
let json = response.body;
return json.rates.USD * amount;
},
For security and transparency reasons, Coda requires that all Packs declare which domains they make requests to. Before your Pack will function property you must add that declaration to your code. The function Your Pack is allowed to access any sub-domains off of this domain, so it's best to select the root domain of the URLs you are making requests to. In this case, use the root domain pack.addNetworkDomain adds a domain to the Pack's declaration. This line can be added anywhere in your code after the boilerplate, but it's usually done at the top of the file.er-api.com instead of narrower API-specific domain of open.er-api.com.import * as coda from "@codahq/packs-sdk";
export const pack = coda.newPack();
pack.addNetworkDomain("er-api.com");
pack.addFormula({
// ...
});
Try it out¶
Now that the Pack is written, let's see it in action.
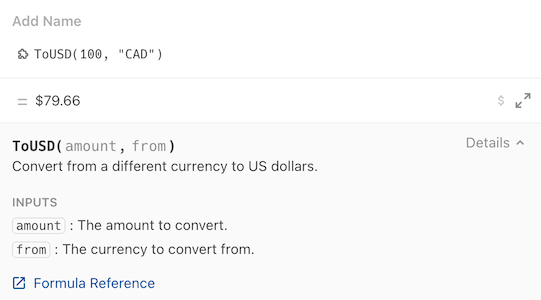
Build the Pack and install it in a doc. Add the ToUSD formula to the page and fill in the parameters.
If everything is working correctly you should get back the currency value converted to dollars.
Bonus points
Try adding autocomplete on the from parameter to provide the user with the list of supported currency codes, and throw an error if they input an invalid one.
View the full code
import * as coda from "@codahq/packs-sdk";
export const pack = coda.newPack();
pack.addNetworkDomain("er-api.com");
pack.addFormula({
name: "ToUSD",
description: "Convert a currency to US dollars.",
parameters: [
coda.makeParameter({
type: coda.ParameterType.Number,
name: "amount",
description: "The amount to convert."
}),
coda.makeParameter({
type: coda.ParameterType.String,
name: "from",
description: "The currency to convert from."
}),
],
resultType: coda.ValueType.Number,
codaType: coda.ValueHintType.Currency,
execute: async function ([amount, from], context) {
let url =
"https://open.er-api.com/v6/latest/" + from;
let response = await context.fetcher.fetch({
method: "GET",
url: url
});
let json = response.body;
return json.rates.USD * amount;
},
});
View the logs¶
Coda logs every API request that your Pack makes, and examining those logs can be very useful when troubleshooting.
In the Pack's side panel click the View logs button to bring up the Pack Maker Tools. If you have navigated away from the Pack's panel, click Insert > Packs > {Pack name}.
Find the most recent invocation of your formula (that isn't from the cache) and expand it to reveal the log entry for the fetch request. Expanding that log entry reveals additional metadata about the request, including the response code and duration.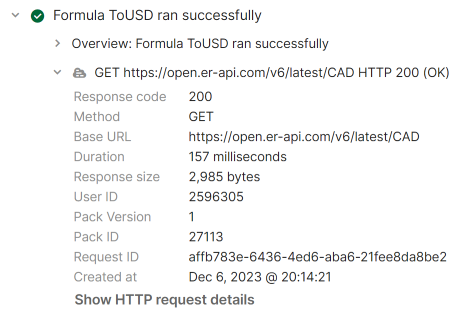
Click the link Show HTTP request details under the log entry to bring up a dialog containing the full HTTP request and response. Expand the response body to inspect the JSON structure that was returned by the API.
Next steps¶
Now that you have an understanding of how to call an external API, here are some more resources you can explore:
- Fetcher guide - More in-depth information about how to use the fetcher.
- Sample code - A collection of sample Packs that show how to use the fetcher.
- Pack maker tools guide - More information on how to view the logs for your Pack.