Return data with meaningful types¶
Pack formulas are written in JavaScript and can return standard JavaScript data types. Coda however supports a wider array of semantic types that change how the data is displayed to the user. When defining a formula or schema you must specify the type of the data being returned.
Value types¶
The core, underlying type of a value is referred to as its value type. The enumeration ValueType defines the set of supported types, and they correspond to basic data types in JavaScript.
For a formula the value type is specified in the resultType property, and for schemas it's specified in the type property. The type specified must match the type of the value returned by your code.
pack.addFormula({
// ...
resultType: coda.ValueType.String,
execute: async function ([], context) {
return "This is a string";
},
});
const MySchema = coda.makeSchema({
type: coda.ValueType.String,
// ...
});
Strings¶
Text values can be returned as JavaScript strings using the String value type.
pack.addFormula({
// ...
resultType: coda.ValueType.String,
execute: async function ([], context) {
return "Hello World!";
},
});
Numbers¶
Number values can be returned as JavaScript numbers using the Number value type.
pack.addFormula({
// ...
resultType: coda.ValueType.Number,
execute: async function ([], context) {
return 42;
},
});
Booleans¶
True or false values can be returned as JavaScript booleans using the Boolean value type.
pack.addFormula({
// ...
resultType: coda.ValueType.Boolean,
execute: async function ([], context) {
return true;
},
});
Objects¶
Structured data can be returned as JavaScript objects using the Object value type. These objects must conform to an defined schema, as specified in the schema property. See the Schemas guide for more information about defining and using schemas.
const MySchema = coda.makeObjectSchema({
properties: {
property1: { type: coda.ValueType.String },
property2: { type: coda.ValueType.Number },
// ...
},
// ...
});
pack.addFormula({
// ...
resultType: coda.ValueType.Object,
schema: MySchema,
execute: async function ([], context) {
return {
property1: "This is a string",
property2: 42,
// ...
};
},
});
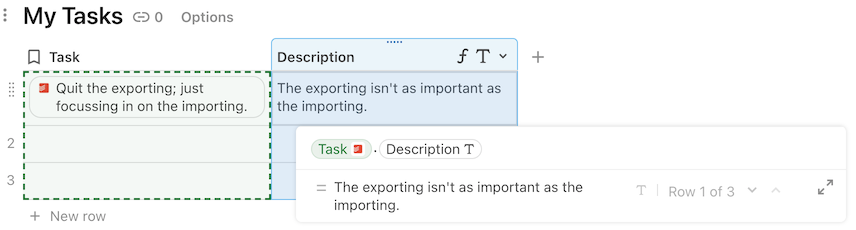
Objects are displayed in the doc as a "chip", a small rectangle with rounded corners. The display value is shown within the chip, with additional properties of object shown on hover.
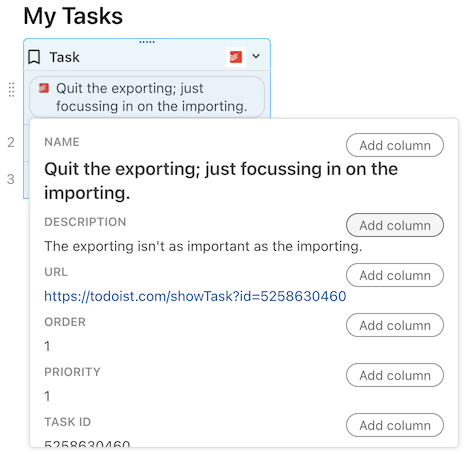
Like Coda tables, the fields within an object can be accessed using dot notation.
Arrays¶
Lists of data can be returned as JavaScript arrays using the Array value type. The resulting array is represented as a List in the Coda formula language.
You must also specify the schema of the items in the array, using the items property. For arrays of simple data you can define the schema inline, supplying only the type key.
pack.addFormula({
// ...
resultType: coda.ValueType.Array,
items: { type: coda.ValueType.String },
execute: async function ([], context) {
return ["This", "is", "a", "string", "array"];
},
});
For arrays of objects, set items to the full object schema.
const MySchema = coda.makeObjectSchema({
properties: {
property1: { type: coda.ValueType.String },
property2: { type: coda.ValueType.Number },
},
// ...
});
pack.addFormula({
// ...
resultType: coda.ValueType.Array,
items: MySchema,
execute: async function ([], context) {
return [
{ property1: "This is a string", property2: 42 },
{ property1: "Another string", property2: 100 },
];
},
});
Value hints¶
To indicate that Coda should display your value in a more meaningful way you can set a value hint. The enumeration ValueHintType defines the set of supported value hints, which correspond to the column formats in Coda. The value hint is set one using the codaType property of a formula or schema. Hints can only be used with certain value types, for example the Percent value hint can only be used with the Number value type.
pack.addFormula({
name: "HalfWayThere",
// ...
resultType: coda.ValueType.Number,
codaType: coda.ValueHintType.Percent,
execute: async function ([], context) {
return 50;
},
});
Markdown¶
The Markdown value hint indicates that Coda should parse the returned string as markdown and render it as rich text. The value can contain basic markdown syntax, but extensions used by other applications (like tables, emoji, etc) are not supported.
pack.addFormula({
// ...
resultType: coda.ValueType.String,
codaType: coda.ValueHintType.Markdown,
execute: async function ([], context) {
return "This is _so_ **cool**!";
},
});
Rendering examples
HTML¶
The Html value hint indicates that Coda should parse the returned string as HTML and render it as rich text. Code only supports a small subset of HTML markup, limited to the basic formatting you can accomplish in markdown.
pack.addFormula({
// ...
resultType: coda.ValueType.String,
codaType: coda.ValueHintType.Html,
execute: async function ([], context) {
return "This is <i>so</i> <b>cool</b>!";
},
});
Rendering examples
Dates and times¶
The Date, Time, and DateTime value hints can be applied to either String or Number values.
When used with a string value, Coda attempts to parse the value, and is able to parse a wide variety of date and time formats. For maximum compatibility however use the ISO 8601 format. When using a JavaScript Date object this can be obtained by calling toISOString(). If the string doesn't include a timezone identifier or offset then Coda will assume it's already in the timezone of the document. See the Timezones guide for more information about how timezones affect return values.
When used with a number value, the number should contain the number of seconds since the Unix epoch (00:00:00 UTC on 1 January 1970). When using a JavaScript Date object this can be obtained by calling getTime() and dividing by 1000.
pack.addFormula({
// ...
resultType: coda.ValueType.String,
codaType: coda.ValueHintType.DateTime,
execute: async function ([], context) {
let now = new Date();
return now.toISOString();
},
});
pack.addFormula({
// ...
resultType: coda.ValueType.Number,
codaType: coda.ValueHintType.DateTime,
execute: async function ([], context) {
let now = new Date();
return now.getTime() / 1000;
},
});
Warning
The Date and Time value hints currently only work correctly within a sync table. When used outside of a sync table both the date and time parts of the returned date will be visible, as if DateTime was used.
Durations¶
The Duration value hint represents an amount of time, rather than a specific time. It can be applied to Number or String values. For numbers, the value represents the number of days (fractional amounts allowed). For strings, the value must match one of a few formats:
| Example | Result | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 6 hours 1 minute 15 seconds | 6 hrs 1 min 15 secs | Full units. |
| 6 hrs 1 min 15 secs | 6 hrs 1 min 15 secs | Abbreviated units. |
| 6 hrs, 1 min, 15 secs | 6 hrs 1 min 15 secs | Commas allowed. |
| 0.25 days, 1 min, 15 secs | 6 hrs 1 min 15 secs | Fractional amounts allowed. |
| 72000 minutes | 50 days | Don't use thousands separators. |
Any duration value your Pack returns will be automatically converted into its most user-friendly form by Coda. For example, 3600 seconds will be shown to the user as 1 hr.
pack.addFormula({
// ...
resultType: coda.ValueType.String,
codaType: coda.ValueHintType.Duration,
execute: async function ([], context) {
return "525600 minutes";
},
});
Percentages¶
Formulas that return a result as a percentage can use the value type Number and the value hint Percent. Return a fraction in your code and the doc will display the equivalent percentage.
pack.addFormula({
// ...
resultType: coda.ValueType.Number,
codaType: coda.ValueHintType.Percent,
execute: async function ([], context) {
return 0.5; // Displayed as "50%" in the doc.
},
});
Images¶
There are two different value hints for image: ImageReference and ImageAttachment. Both of these are applied to string values, where the string contains the URL of the image. For image references, the image is always loaded from the source URL. For image attachments, Coda copies the image from the source URL into the document and shows that local copy.
Image attachments should be used in most cases. An image reference may make more sense if you expect the image to be updated often and want to ensure the doc is always using the latest copy, or when contractually obligated to hotlink to the image.
pack.addFormula({
// ...
resultType: coda.ValueType.String,
codaType: coda.ValueHintType.ImageReference,
execute: async function ([], context) {
return "https://via.placeholder.com/150";
},
});
Bug
Image attachments currently only work correctly within a sync table. When used outside of a sync table they behave like image references and load the image from the source URL.
Files¶
Similar to ImageAttachment mentioned above, you can return other file types using the value hint Attachment. This hint is also applied to string values, where the string contains the URL of the file. Coda copies the file from the source URL into the document and uses that local copy.
const DealSchema = coda.makeObjectSchema({
properties: {
// ...
contract: {
type: coda.ValueType.String,
codaType: coda.ValueHintType.Attachment,
},
},
// ...
});
Bug
Attachments currently only work within a sync table. Additionally, file attachments may be shown with the wrong file name.
Select lists¶
The SelectList value hint can be used to render the property as a select list. It is only supported in sync tables, and is most useful in those that support two-way sync.
It can be applied to properties of type String or Object. The possible options of the select list are set in the options field, which can contain an array of values or a function that generates them.
const ShirtSchema = coda.makeObjectSchema({
properties: {
size: {
type: coda.ValueType.String,
codaType: coda.ValueHintType.SelectList,
options: ["S", "M", "L", "XL"],
},
// ...
},
// ...
});
To allow multiple selections, wrap the schema in an outer Array schema.
const OrderSchema = coda.makeObjectSchema({
properties: {
sizes: {
type: coda.ValueType.Array,
items: {
type: coda.ValueType.String,
codaType: coda.ValueHintType.SelectList,
options: ["S", "M", "L", "XL"],
},
},
// ...
},
// ...
});
See the Two-way Sync guide for more information about property options.
Embedded content¶
The Embed value hint can be used to embed external content in the Coda doc. This value hint can be applied to String values, where the string contains the URL to the external content.
pack.addFormula({
// ...
resultType: coda.ValueType.String,
codaType: coda.ValueHintType.Embed,
execute: async function ([], context) {
return "https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oLYZv68M3Kg";
},
});
Read the Embedding content guide to learn more.
People¶
The Person value hint can be used to @-reference a Coda user account. This hint can be applied to Object values, where the object has a property that specifies the user's email address. The email address must be contained within the property of the object that is listed as its idProperty within the schema definition, and that property must be marked as required.
const MyPersonSchema = coda.makeObjectSchema({
codaType: coda.ValueHintType.Person,
properties: {
name: { type: coda.ValueType.String },
email: { type: coda.ValueType.String, required: true },
},
displayProperty: "name",
idProperty: "email",
});
When no Coda user with the given email address is found the object will render as a normal object chip.
Warning
This value hint currently only work correctly within a sync table. When used outside of a sync table it will render as a normal object chip, as if no value hint was applied.
Row reference¶
The Reference value hint can be used to reference a row in a sync table. See the Schemas guide for more information about defining and using schema references.
Warning
This value hint currently only work correctly within a sync table. When used outside of a sync table it will render as a normal object chip, as if no value hint was applied.
Corresponding column types¶
The columns of a Coda table are strongly typed, and the data types in the Pack SDK roughly correspond to those same types. The table below indicates the value type and value hint that corresponds to a each column type.
| Column type | Supported | Value type | Value hint | Options |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Text | ✅ Yes | String |
||
| Link | ✅ Yes | String |
Url |
LinkSchema |
| Embed1 | ✅ Yes | String |
Embed |
StringEmbedSchema |
| Canvas | ❌ No | |||
| Select list | ✅ Yes | String orObject |
SelectList |
StringWithOptionsSchema orObjectSchemaDefinition |
| Number | ✅ Yes | Number |
NumericSchema |
|
| Percent | ✅ Yes | Number |
Percent |
NumericSchema |
| Currency | ✅ Yes | Number |
Currency |
CurrencySchema |
| Slider | ✅ Yes2 | Number |
Slider |
SliderSchema |
| Progress | ✅ Yes2 | Number |
ProgressBar |
ProgressBarSchema |
| Scale | ✅ Yes2 | Number |
Scale |
Scalechema |
| Date | ✅ Yes | String orNumber |
Date |
StringDateSchema orNumericDateSchema |
| Time | ✅ Yes | String orNumber |
Time |
StringTimeSchema orNumericTimeSchema |
| Date and time | ✅ Yes | String orNumber |
DateTime |
StringDateTimeSchema orNumericDateTimeSchema |
| Duration | ✅ Yes | String orNumber |
Duration |
DurationSchema orNumericDurationSchema |
| Checkbox | ✅ Yes2 | Boolean |
||
| Toggle | ✅ Yes2 | Boolean |
Toggle |
|
| People | ✅ Yes | Object |
Person |
|
| ✅ Yes | String |
Email |
EmailSchema |
|
| Reaction | ❌ No | |||
| Button | ❌ No3 | |||
| Image | ✅ Yes | String |
ImageAttachment |
ImageSchema |
| Image URL | ✅ Yes | String |
ImageReference |
ImageSchema |
| File | ✅ Yes | String |
Attachment |
|
| Relation | ✅ Yes | Object |
Reference |
Formatting options¶
Some value types and hints support additional formatting options. For example, Number types support a precision option that controls how many decimal places to show, and Currency supports a currencyCode option that determine the currency symbol to show. These options are set in a schema, and for a formula result this may meaning adding a schema property to the formula definition.
pack.addFormula({
name: "GetPrice",
// ...
resultType: coda.ValueType.Number,
schema: {
type: coda.ValueType.Number,
codaType: coda.ValueHintType.Currency,
currencyCode: "EUR",
precision: 2,
},
// ...
});
const PriceSchema = coda.makeSchema({
type: coda.ValueType.Number,
codaType: coda.ValueHintType.Currency,
currencyCode: "EUR",
precision: 2,
});
The full set of formatting options for a given value type and hint can be found in the Options column of the table above.
-
Embed isn't a column type in Coda, but it can be used in a table or on the canvas to embed content. ↩
-
Control column types will only render correctly in a sync table, and will not be interactive. ↩↩↩↩↩
-
While a Pack can't return a button directly, it can provide actions that a user can use to power their buttons. ↩