Authenticating using Amazon Web Services¶
APIs that are part of Amazon Web Services (AWS) use a proprietary authentication scheme known as AWS Signature Version 4. Coda provides built-in support for this type of authentication, and to set it up you only need to write a few lines of simple code. You must specify which AWS service you are connecting to, and each Pack can only connect to a single service.
The SDK supports two different ways of authenticating with an AWS service: access keys and by assuming a role.
Access key¶
The simplest method of authentication requires that the Coda user provides an access key and secret associated with an AWS user. Coda will use these values to sign outgoing requests. Simply set the authentication type to AWSAccessKey and specify the AWS service you are connecting to.
pack.setUserAuthentication({
type: coda.AuthenticationType.AWSAccessKey,
service: "s3",
});
When authenticating, the user will be prompted to enter their access key and secret.
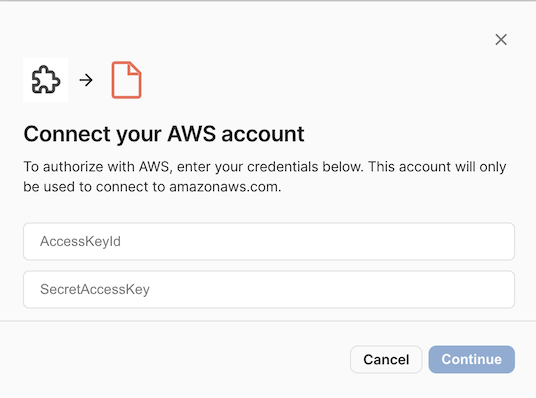
You can learn more about how to generate access keys in the AWS documentation.
Assume role¶
A more secure way to authenticate is by using the AssumeRole feature of the Security Token Service (STS). Trust is first established between the AWS user running Packs code and a role you created in your AWS account. When the Pack is run, temporary credentials are generated and used to sign outgoing requests.
To use this form of authentication, simply set the authentication type to AWSAssumeRole and specify the AWS service you are connecting to.
pack.setUserAuthentication({
type: coda.AuthenticationType.AWSAssumeRole,
service: "s3",
});
When authenticating, the user will be prompted to enter the Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of the role to assume, as well as an associated external ID.
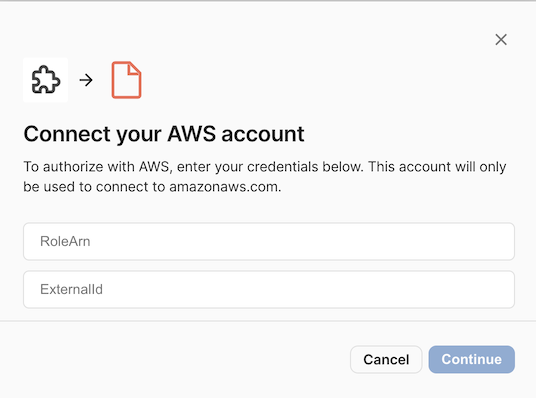
You can learn more about how to create roles in the AWS documentation.
Trust policy¶
In addition to supplying the role and external ID, the user authenticating the Pack must also create a trust relationship between Coda's AWS account and their role. This is done by setting a trust policy on the role, associating the role with the account and an external ID.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "GrantCodaPackAssumeRole",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": [
"arn:aws:iam::029208794193:root"
]
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"sts:ExternalId": "<PACK_ID>:<EXTERNAL_ID>"
}
}
}
]
}
Coda's AWS account has the ID arn:aws:iam::029208794193:root, and this is same for all Packs.
The external ID condition is used as a security measure, to ensure that other Packs can't also use the role. When signing a request, Coda will prepend the Pack ID to the user-supplied external ID value, with the format <PACK_ID>:<EXTERNAL_ID>. While AWS doesn't strictly require an external ID to use the AssumeRole flow, it is recommended for cross-account access scenarios like this and Coda enforces it as a best practice.
Running locally¶
If you are developing your Pack locally using the CLI, when you run your Pack using coda execute it won't be running under Coda's AWS account. Instead you'll need to create your own AWS user and setup your local environment to use it.
First update your policy to include the ID of the user you created.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "GrantCodaPackAssumeRole",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": [
"arn:aws:iam::029208794193:root",
"<ARN_OF_USER>"
]
},
// ...
}
]
}
Then generate an access key and secret for the user, and pass these using the environment variables AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY respectively.
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID="<ACCESS_KEY>" AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY="<SECRET>" \
npx coda execute pack.ts <FormulaName>
You can alternatively use the AWS CLI to manage these credentials for you.