Private Beta
Building, testing, and publishing agents are only available to a limited set of developers at this time.
The following documentation provides an early preview of the SDK, and the specifics are subject to change.
Upgrade an existing Pack to an agent¶
If you've already built a Pack for Coda, the good news is that it can be easily upgraded to a Superhuman Go agent. All agents are Packs under the hood, and with some minor tweaks, your existing Pack can be one too.
You don't need to be an AI expert to do this, as we provide the LLM and hook it up to your Pack. It's done automatically, so you can install your Pack in Superhuman Go and start chatting with it right away.
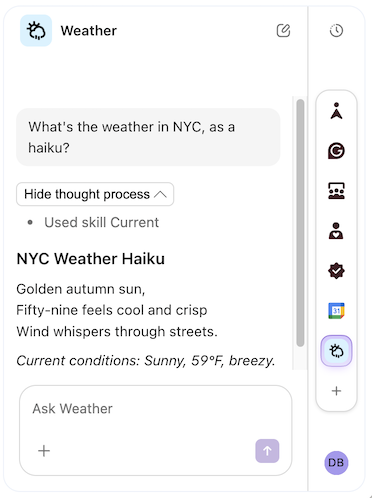
In the screenshot above, you can see a user chatting with the Weather Pack, which hasn't had any code changes. The LLM knows all the formulas and actions in the Pack, calls them as needed, and displays the results in a human-friendly way.
How well your Pack works as an agent can vary, so the main task is to test it as an agent and update it as needed to ensure a great user experience.
Recommended updates¶
There aren't strict requirements for your Pack to work as an agent, but there are common patterns. Below is a list of updates to consider.
Remove doc-specific language¶
Packs used to only run in docs, but now agents can be run anywhere. Update your Pack to remove doc-specific language, including:
-
Building block descriptions
- "Syncs your tasks to your doc"
- "Sync your tasks"
-
Parameter descriptions
- "The time zone of your doc"
- "The current time zone"
Add indexing to your sync tables¶
The data in your sync tables won't be available to the agent unless you index them. You should set up indexing for sync tables that:
- Have at least one free-text column (description, notes, body, etc.)
- Have a link column
See the Indexing guide for more information on adding indexing features to your sync table, and the Developing & testing guide for testing.
Add chat skills where appropriate¶
A default chat skill is generated for every Pack, meaning you can chat with your Pack right away. It has access to all of the formulas, actions, and indexed knowledge in your Pack.
While the default chat skill can handle a wide range of user questions and prompts, it may struggle with the more nuanced tasks. In those cases, you should add additional skills to your Pack, providing a custom prompt that better guides the LLM.
See the Skills guide for more information on how to add custom skills.
Utilize suggestions¶
One of Grammarly's most powerful features is to see what the user is writing and make suggestions on how to improve it. The same suggestion UI is available to agents.
Look for potential use cases where making a writing suggestion would be beneficial—for example, filling in a placeholder or providing additional context about a term or phrase.
See the Screen annotation tools section guide for more information.
Adding features for agents only¶
During the upgrade process, you may need to adjust your Pack to work better with the LLM. You'll want to avoid breaking the experience for existing users of your Pack, and there are tactics to do so.
Hidden formulas¶
You can add a new formula just for the LLM to use by adding isExperimental: true to the definition. These won't be displayed to users in Coda docs, but will be made available to the LLM to call.
pack.addFormula({
name: "GetWorkspaceId",
description: "Gets the ID of the user's workspace.",
parameters: [],
resultType: coda.ValueType.String,
// Hide this in Coda docs, but allow the LLM to use it.
isExperimental: true,
execute: async function (args, context) {
// ...
},
});
LLM instructions¶
The LLM uses the formula and parameter descriptions to understand how to use them, but sometimes the agent needs more information to call them reliably. You can provide an alternate description just for the LLM to use by setting the instructions field on the formula or parameter.
pack.addFormula({
name: "CreateContact",
description: "Creates a new contact.",
instructions: `
Creates a new contact for a given customer.
The contact should be an individual who works at the company.
To save the contact information for the business as a whole, use the
UpdateCustomer formula instead.
`,
parameters: [
coda.makeParameter({
type: coda.ParameterType.String,
name: "name",
description: "The name of the contact.",
instructions: `
The name of the contact.
If available, provide the full name (first, middle, and last).
Don't include prefixes and suffixes (Dr., Esq., etc.).
`,
}),
// ...
],
resultType: coda.ValueType.String,
execute: async function (args, context) {
// ...
},
});
Alternate suggested parameter values¶
Since sync tables are limited to 10,000 rows in docs, you may have added parameters for limiting the scope of the sync, perhaps with a suggestedValue that populates a reasonable default. When used by an agent to index data, however, the sync table can sync many more rows, and it would be better to use a different suggested value that includes a broader scope.
This can be done by setting the field ingestionSuggestedValue on the parameter. This suggested value will only be used in the agent setup UI.
pack.addSyncTable({
name: "Tickets",
// ...
formula: {
// ...
parameters: [
coda.makeParameter({
type: coda.ParameterType.DateArray,
name: "created",
description: "Include tickets created within the given time range.",
suggestedValue: coda.PrecannedDateRange.Last30Days,
ingestionSuggestedValue: coda.PrecannedDateRange.Last365Days,
}),
],
execute: async function (args, context) {
// ...
},
},
});
Source application detection¶
While uncommon, there may be times when you want to adjust the logic in your code depending on whether it's running in a doc or an agent. You can do that by looking at the InvocationSource value in the context.invocationLocation.source.
pack.addFormula({
name: "SendEmail",
// ...
execute: async function (args, context) {
// ...
let emailFooter;
let source = context.invocationLocation.source;
switch (source) {
case coda.InvocationSource.Doc:
emailFooter = "Sent from Coda.";
break;
case coda.InvocationSource.Go:
emailFooter = "Sent from Superhuman Go.";
break;
default:
throw new Error("Unknown invocation source: " + source);
}
// ...
},
});
Known limitations¶
Currently, some Pack features don't work in agents.
- parameter
autocomplete- The LLM can't see the possible autocomplete values for a parameter. If the list of possible values is small, include them in the parameter description. varargparameters - The LLM can't setvarargparameters. As a workaround, add a hidden formula that uses a JSON string parameter instead.ConnectionRequirement.Optional- If user auth is defined, users will need to sign in before they can use the agent at all.- Two-way sync - Agents can't edit records using two-way sync. As a workaround, add an action formula that can update a record.