Private Beta
Building, testing, and publishing agents are only available to a limited set of developers at this time.
The following documentation provides an early preview of the SDK, and the specifics are subject to change.
Give your agent access to tools¶
Agent skills can be provided with a set of tools, which the LLM can choose to leverage. There are a few types of tools:
Pack- Allow the LLM to run a Pack formula, which can calculate a value or take an action.Knowledge- Allow the LLM to query previously indexed records from the knowledge layer.ScreenAnnotation- Allow the LLM to draw on the user's doc or screen.
Pack tools¶
One of the basic building blocks of a Pack is a formula. Like an Excel formula, it takes a set of inputs and calculates an output. These formulas can also make network requests, enabling them to fetch and send data to external APIs or servers. You can read more about them in the Formulas guide.
All formulas¶
By default, a Pack tool includes all the formulas in that Pack.
pack.addSkill({
name: "Calculator",
// ...
tools: [
// All the formulas in this Pack.
{ type: coda.ToolType.Pack },
],
});
pack.addFormula({
name: "GCD",
description: "Calculates the greatest common divisor for a set of numbers.",
// ...
});
pack.addFormula({
name: "LCM",
description: "Calculates the least common multiple for a set of numbers.",
// ...
});
Specific formulas¶
You can limit which formulas the skill has access to by specifying the formulas field of the tool. This can be useful when you want to focus the LLM on a specific set of tools, as too many tool options can lead to worse results.
pack.addSkill({
// ...
tools: [
{
type: coda.ToolType.Pack,
formulas: [
{ formulaName: "GCD" },
],
},
],
});
Actions¶
Formulas that have side effects (e.g., create or update records in an API) should be annotated as actions (isAction: true). Unlike regular formulas, action formulas require confirmation before they are run. Learn more in the Actions guide.
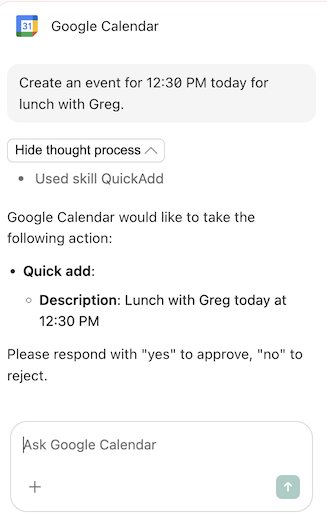
Knowledge¶
Agent skills can reference previously indexed knowledge, enabling fast, accurate retrieval of relevant information. It's stored in our knowledge layer, a vector database with permission-aware retrieval. It enables retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), enabling the LLM to work with private data without being trained on it.
Agents can add knowledge by including a sync table with some special properties set. Refer to the Indexing guide for more information on how to set up your agent to add knowledge to the index.
Limited information available to the LLM
Although a sync table row can contain many properties, only a select set of that information will be available to the LLM when it's retrieved. Specifically:
- A chunk of text that semantically matches the user's question, from one of the properties in
index.properties. - The values only of properties listed in
index.contextProperties. - The value of
titleProperty. - The value of
linkProperty.
The value of other properties in the schema can't be accessed.
Pack knowledge¶
When you specify the knowledge source type as Pack, you give your skill access to all of the indexed knowledge across all sync tables in the same Pack.
pack.addSkill({
name: "TodoList",
// ...
tools: [
{
type: coda.ToolType.Knowledge,
source: { type: coda.KnowledgeToolSourceType.Pack },
},
],
});
pack.addSyncTable({
name: "Projects",
// ...
});
pack.addSyncTable({
name: "Tasks",
// ...
});
Screen annotation tools¶
These tools allow the LLM to annotate text in the user's doc or on the user's screen, providing additional information, suggested changes, etc.
Rewrites¶
This tool allows your agents to suggest changes to the user's writing, just like the traditional Grammarly grammar assistant.
pack.addSkill({
name: "SoundLikeYoda",
displayName: "Sound like Yoda",
description: "Make your text sound like Yoda from Star Wars.",
prompt: `
Suggest changes to the writing to make it sound like Yoda from Star Wars.
Use the Rewrite tool to make those suggestions.
Only make a single call to the Rewrite tool, passing in all suggestions.
Only pass in one rewrite per paragraph, combining all the changes.
`,
tools: [
{
type: coda.ToolType.ScreenAnnotation,
annotation: { type: coda.ScreenAnnotationType.Rewrite },
},
],
});
When the tool runs, blue bars are added to the left of the affected paragraphs. Hovering over them reveals the alternative text the agent suggested, which users can accept or reject.
Under the hood, the rewrite tool has the following input format:
[
{
"originalText": "<original text",
"replacementText": "<suggested text>",
"explanation": "<why the change matters>",
"paragraphId": "<id of paragraph containing original text>"
}
]
While the LLM can fill in these inputs on its own, you may want to suggest a specific format for the explanation and related details.
Multiple calls or rewrites for the same paragraph not supported
If your agent calls the suggestion tool more than once, only the last call will be used. It's recommended to add language to your prompt that encourages the LLM to call it only once.
Only make a single call to the Rewrite tool, passing in all suggestions.
Additionally, it's only expecting a single suggestion per paragraph, and passing in more than one can lead to suggestions not displaying correctly. Use language in your prompt to encourage the LLM to merge multiple suggestions for the same paragraph.
Only pass in one rewrite per paragraph, combining all the changes.
Contact resolution tool¶
While indexing records into the knowledge layer, agents can separately index the people mentioned in those records. The resulting contacts, from all agents that index them, are pooled together and made available to every other agent the user has installed.
Your agent can search these contacts using the contact resolution tool. With this tool, your users can mention people by name instead of typing their email addresses.
For example, if the user types "Assign the ticket to Alice" your agent can search their contacts, perhaps from Gmail and other agents they have installed, to determine that Alice is alice@example.com. Your agent can then continue with other tool calls that require the email address.
To allow your agent to search these contacts, add the ContactResolution tool to the desired skills.
pack.setChatSkill({
name: "Chat",
displayName: "Chat",
description: "The root chat skill.",
prompt: `
When the user mentions someone by name, but an email address is needed,
use the Contact Resolution tool to look up the contact.
`,
tools: [
{ type: coda.ToolType.ContactResolution },
{ type: coda.ToolType.Pack },
],
});
Each contact has a name and email address only; it's not possible to retrieve other information about a contact. To learn more about how to index contacts within your agent, see the Indexing schemas guide.
MCP Tools¶
Agents that connect to an MCP can use any of the tools it provides.
pack.addSkill({
name: "RandomIcon",
// ...
tools: [
{ type: coda.ToolType.MCP },
],
});
pack.addMCPServer({
name: "Icons8",
endpointUrl: "https://mcp.icons8.com/mcp/",
});
Learn more about connecting to an MCP server in the MCP guide.