Share
Explore

Workflow: Churn Detection and Prevention
Define your churn indicators
Start by identifying the key indicators that can signal potential churn, such as a decrease in product usage, low engagement with support content, or lack of communication with your team.
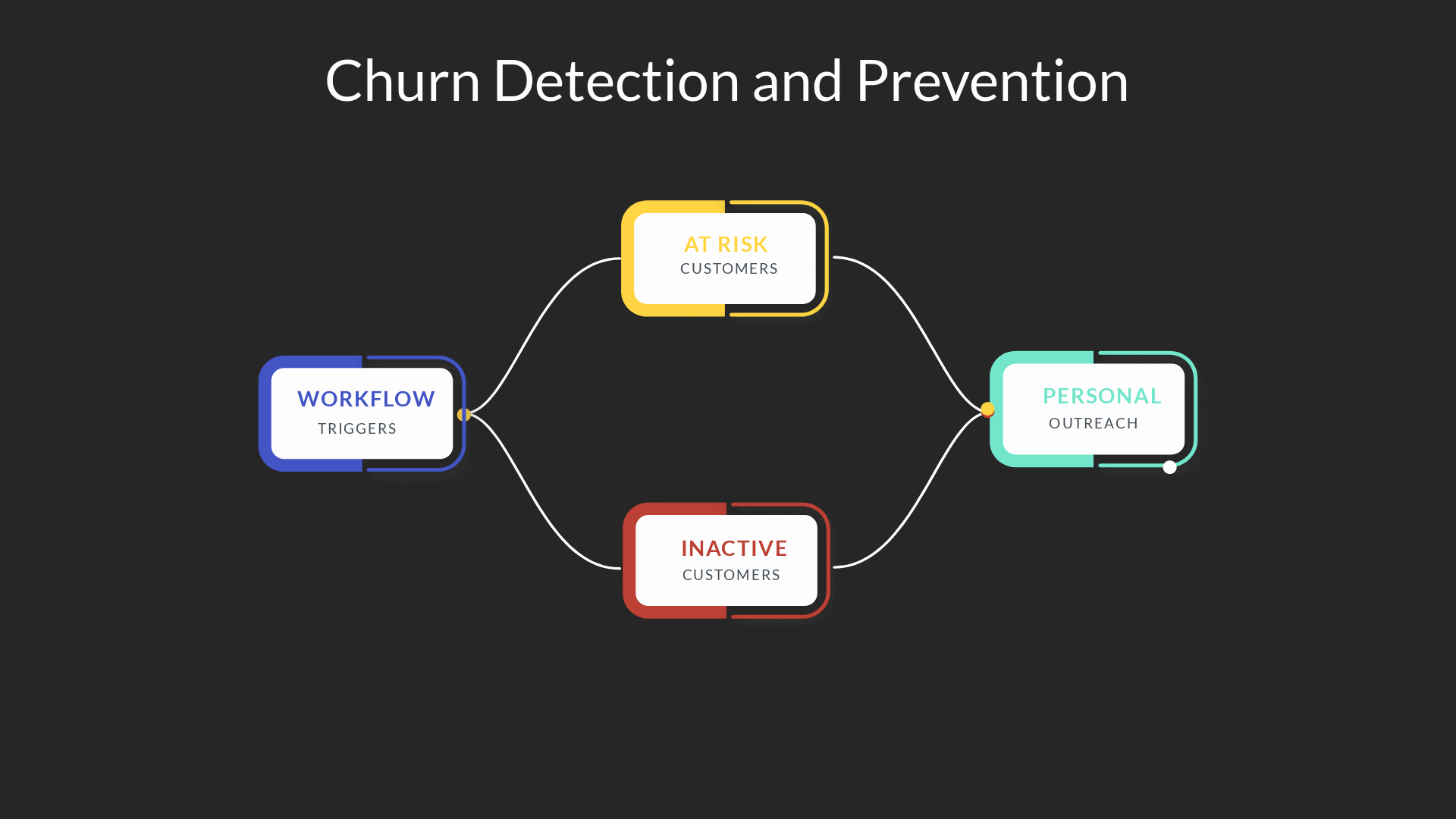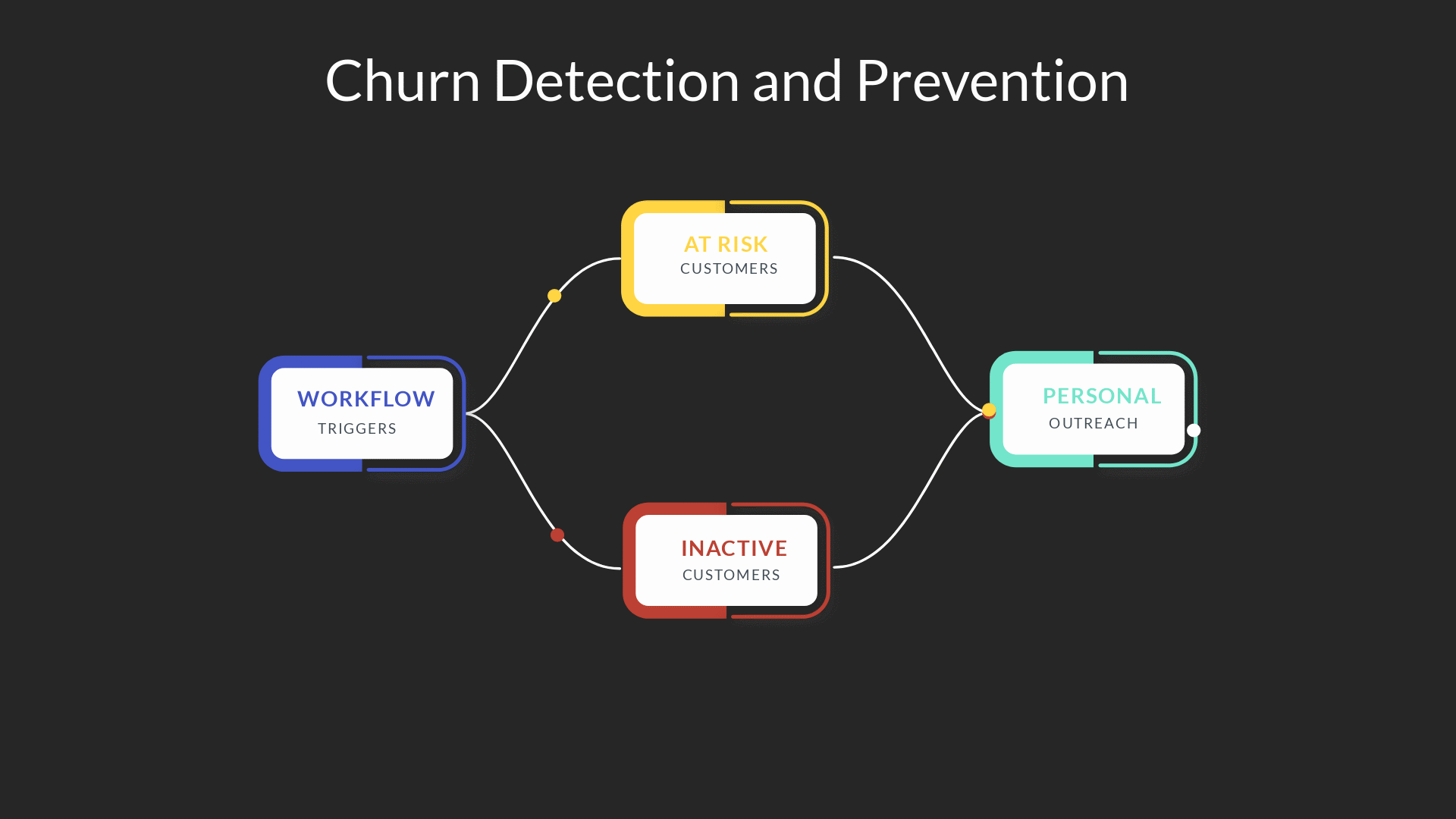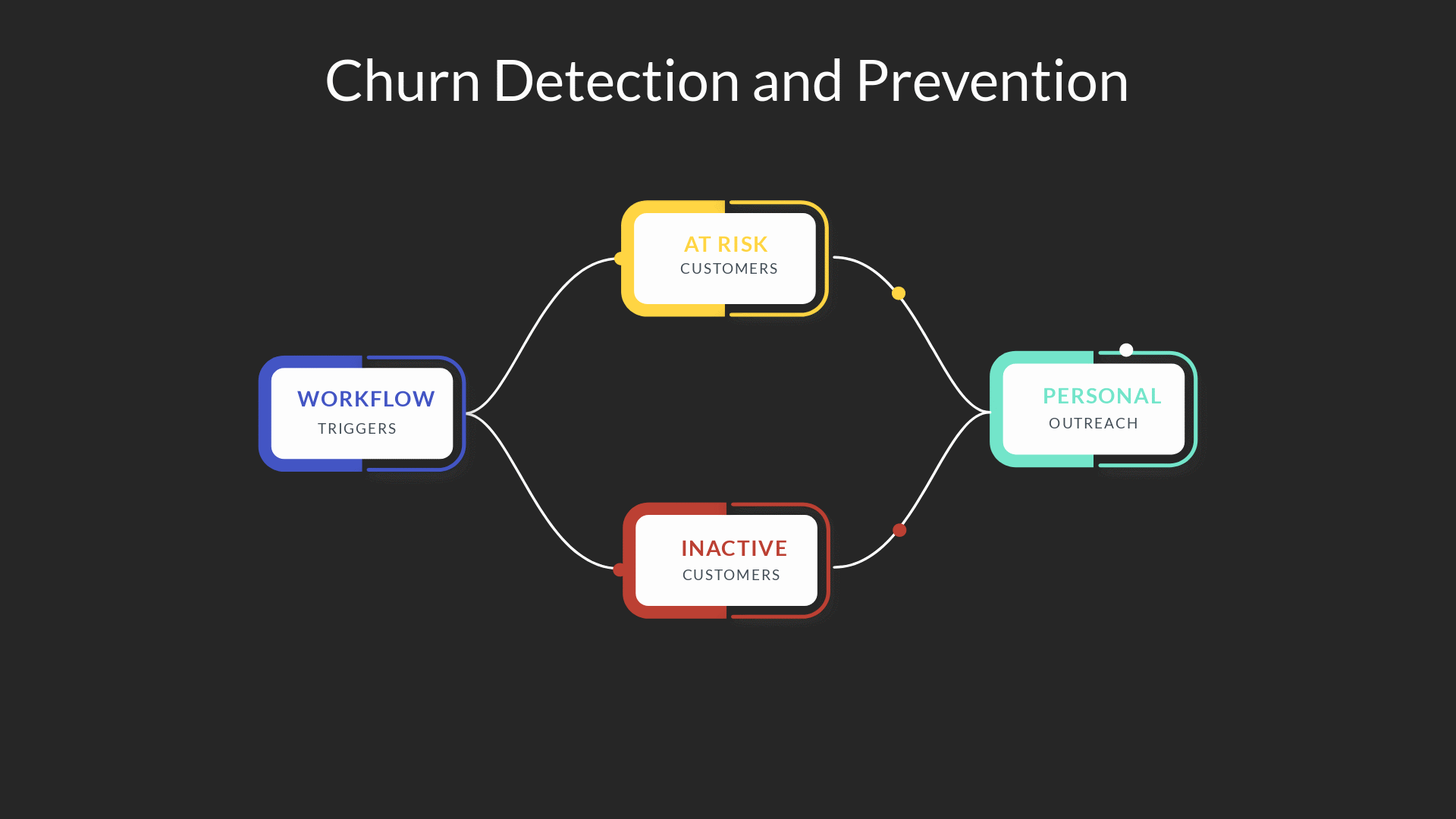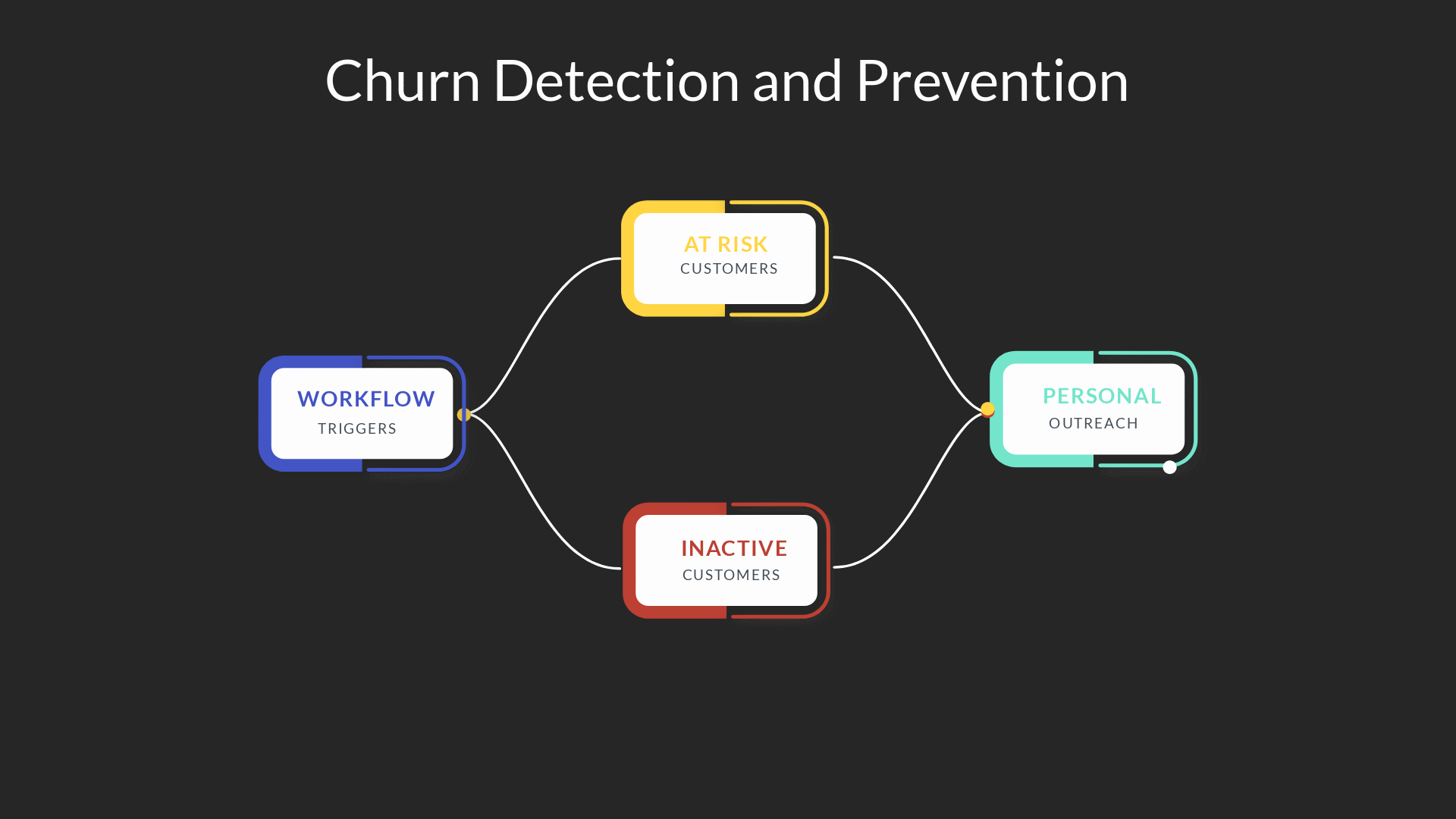

You can use CRM for your contact properties, custom properties, and events to track these indicators.
Decreased product usage
A significant drop in a customer's usage of your product could indicate dissatisfaction or that they need to find value in the service.
Track metrics such as login frequency, feature usage, and session duration to identify customers who may be disengaging.
Low engagement with support content
If a customer is not engaging with your help resources or support content, they may be struggling to understand or use your product effectively.
Track interactions with knowledge base articles, webinars, or other educational materials to identify customers who may need additional assistance.
Negative customer feedback
Keep track of customer feedback, whether it's from support tickets, surveys, or social media. A pattern of negative feedback or dissatisfaction could be a strong churn indicator.
Billing issues
Late payments, multiple declined transactions, or a downgrade in subscription level may indicate financial concerns or a lack of perceived value in your product.
Monitor billing activity closely to identify customers who may be at risk of churning.
Lack of communication
Customers who rarely interact with your team or who have stopped responding to your communications could be at risk of churning. Track email opens, replies, and other interactions to identify these customers.
Inactivity or disengagement with marketing emails
If a customer stops opening or clicking through your marketing emails, it could be a sign that they're losing interest in your product.
Monitor email engagement metrics to identify customers who may need a more targeted approach to re-engage them.
Support ticket frequency
An increase in support requests, especially for the same issue, could indicate frustration with your product.
Track the frequency and nature of support tickets to identify customers who may be experiencing challenges.
Low Net Promoter Score (NPS)
A low NPS score is a sign that a customer is not likely to recommend your product to others.
Monitor your NPS scores and follow up with customers who have low ratings to understand their concerns and address them.
Product-related issues
Frequent bugs, downtime, or performance issues can lead to customer dissatisfaction and potential churn. Monitor your product's performance and address issues promptly to maintain customer satisfaction.
Want to print your doc?
This is not the way.
This is not the way.

Try clicking the ⋯ next to your doc name or using a keyboard shortcut (
CtrlP
) instead.